Abstract
Background Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBL) is a rare mature aggressive large B-cell lymphoma (aLBCL) arising in the mediastinum, affecting young adults, with distinctive clinical and biological features. Optimal first-line therapy for PMBL is more controversial than other subtypes of aLBCL. Therapeutic options include standard R-CHOP21 or more intensive regimens (R-CHOP14, R-ACVBP or DA-EPOCH-R) possibly followed by mediastinal consolidative radiation therapy (CRT). Here we report the results on PMBL included in a pooled analysis of 5 LYSA prospective clinical trials for aLBCL.
Methods Between 2003 and 2015, the LYSA conducted 5 prospective clinical trials for patients (pts) < 60-65 years with aLBCL. LNH03-1B (NCT00140660) randomized ACVBP vs R-ACVBP in pts with localized low-risk aLBCL (Ketterer N, Ann Oncol 2013); LNH03-2B (NCT00140595) randomized R-CHOP21 vs R-ACVBP in pts with age-adjusted international prognostic index (aaIPI) equal to 1 (Recher C, Lancet 2011); LNH03-3B assessed R-ACVBP and consolidative autologous stem-cell transplantation (ASCT) in high-risk aLBCL (Fitoussi O and Belhadj K, Haematologica 2011); LNH07-3B randomized R-CHOP14 vs R-ACVBP and assessed a PET-driven consolidation strategy in aaIPI2-3 pts (Casasnovas RO, Blood 2017); GAINED study randomized obinutuzumab vs rituximab in aaIPI1-3 pts treated with CHOP14 or ACVBP (Le Gouill S, Blood 2021). None of these trials included CRT. For the purpose of the pooled analysis, PMBL cases were extracted based on clinical presentation, initial pathologic diagnosis and central pathology review. The primary endpoints were 4-year PFS and OS according to first-line treatment (R-CHOP21, R-CHOP14 and R-ACVBP) in pts < 65 years with PMBL. Secondary endpoints included the comparison of aaIPI, IPI, and NCCN-IPI for prognostication, the number of permanent treatment discontinuation for toxicity, and the impact of consolidative ASCT.
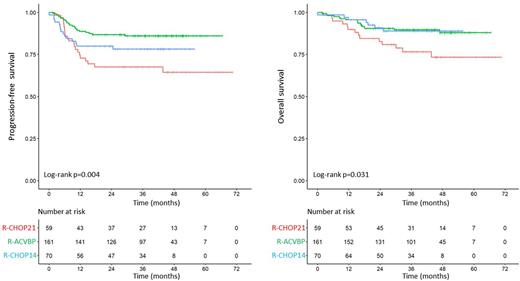
Results Among 1177 pts included in clinical trials and treated with R-chemo, 290 had PMBL (8 LNH03-1B, 112 LNH03-2B, 47 LNH03-3B, 44 LNH07-3B, 79 GAINED). Median age was 35 years (18-63), with a female predominance (53%). Central pathology review was performed in 270 cases (93%). Overall, aaIPI was 0, 1, 2 and 3 in 10, 147, 103 and 29 pts, respectively; IPI was low, low-intermediate, high-intermediate, and high in 144, 62, 64 and 19 pts; and NCCN-IPI was low, low-intermediate, high-intermediate, and high in 76, 171, 43 and 0 pts. In all, 59 pts received R-CHOP21, 70 R-CHOP14 and 161 R-ACVBP, without significant difference in baseline characteristics. 82 pts underwent consolidative ASCT. After a median follow-up of 42 months, 4-y PFS and OS of the 290 pts were 80% and 85%, respectively. There were 57 PFS events including 49 progression/relapse events and 8 deaths without progression/relapse. There were 38 deaths, 28 (74%) of lymphoma, 4 (11%) of toxicity, and 6 (16%) of other causes. Given the low number of events for PFS and OS, aaIPI, IPI and NCCN-IPI scores were each dichotomized. NCCN-IPI had the best prognostic impact with 4-y PFS of 82% (low + low-intermediate) vs 67% (high-intermediate + high, p=0.01), and 4-y OS of 86% vs 78% (p=0.05). For patients treated with R-CHOP21, R-CHOP14 and R-ACVBP, 4-y PFS was 64%, 78% and 86% (p=0.004), and 4-y OS was 73%, 89% and 88% (p=0.031), respectively. In multivariate analysis including NCCN-IPI and treatment, both factors remained independently prognostic for PFS and OS. For PFS: NCCN-IPI (reference low + low-intermediate) HR 3.1 [95% CI 1.6-6, p<0.001]; treatment (reference R-CHOP21), R-CHOP14 (HR 0.468 [95% CI 0.228-0.960, p=0.04]), R-ACVBP (HR 0.277 [95% CI 0.144-0.533, p<0.001]). For OS: NCCN-IPI HR 3.1 [95% CI 1.4-7.1, p=0.007]; treatment, R-CHOP14 (HR 0.315 [95% CI 0.120-0.826, p=0.02]), R-ACVBP (HR 0.316 [95% CI 0.146-0.682, p=0.003]). Permanent treatment discontinuation for toxicity occurred in 5 pts (all in R-ACVBP group). Consolidative ASCT did not improve survival.
Conclusion In this pooled analysis of LYSA prospective trials, R-CHOP14 and R-ACVBP significantly improved PFS and OS compared to R-CHOP21. There was more permanent treatment discontinuation for toxicity with R-ACVBP, thus R-CHOP14 without CRT may be a preferred option for young pts with PMBL.
Disclosures
Sibon:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Belhadj:BMS, JANSSEN, SANOFI, AMGEN, ABBVIE: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel for ASH, ASCO and EHA Annual Meeting. Ghesquieres:BMS: Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria. Morschhauser:Janssen: Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Miltenyi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Allogene therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Epizyme: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Genmab: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Le Gouill:Novartis, Kite/Gilead, Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel support.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal